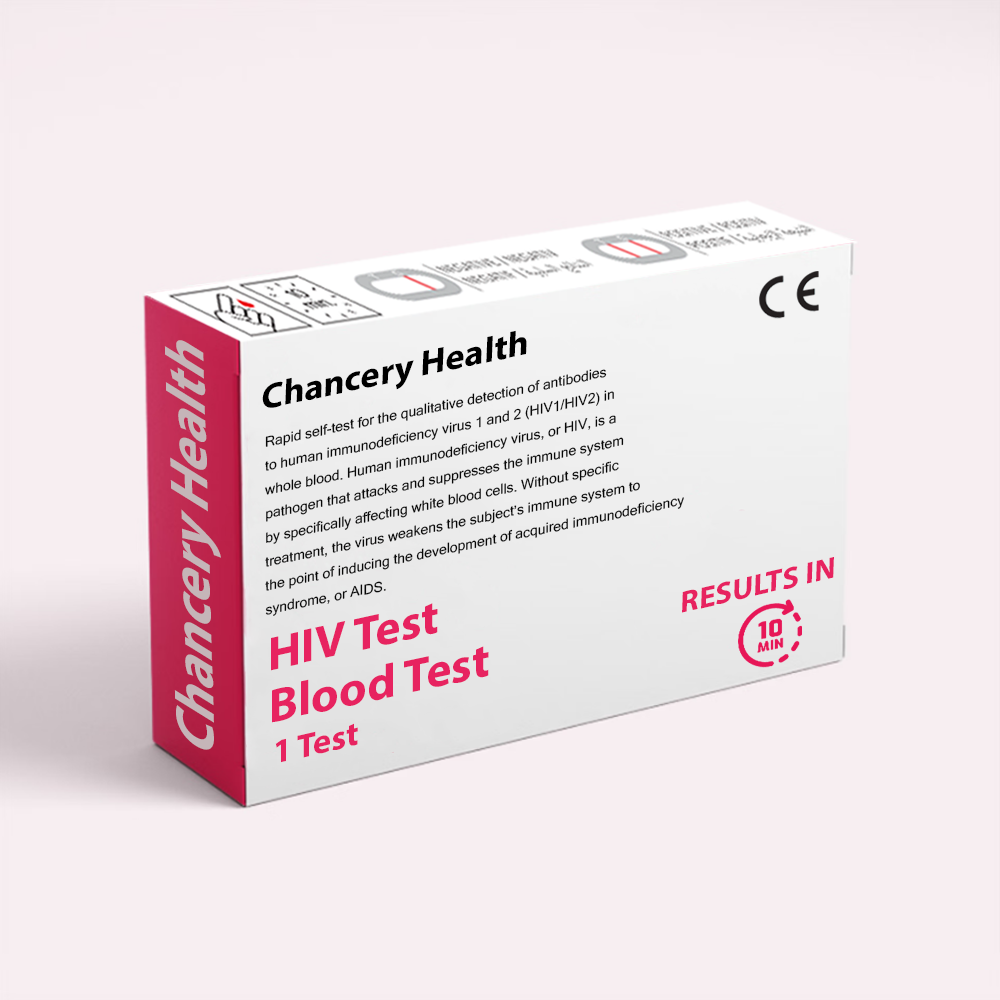
Description
Human immunodeficiency virus, or HIV, is a pathogen that attacks and suppresses the immune system by specifically affecting white blood cells. Without specific treatment, the virus weakens the subject’s immune system to the point of inducing the development of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, or AIDS. It is a syndrome that can occur in people with HIV even several years after the infection, when the immune system’s efficiency dramatically falls, and the body loses its ability to fight even the most common infections.